Topics to be Learn:
- Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction in animals
- Sexual Reproduction in animals
- Menstrual cycle (Ovarian cycle)
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization / Syngamy
- Embryonic development
- Pregnancy / Gestation
- Placenta
- Parturition
- Lactation
- Reproductive Health
- Birth control
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
- Infertility
Reproduction:
- Definition: Biological process forming new life from similar existing life.
- Ensures species survival over time.
- Methods: Asexual and sexual.
Asexual Reproduction in Animals:
Characteristics:
- Common and primitive.
- No meiosis or gamete formation/fertilization.
- Involves single parent.
- Offspring identical to parent (clone).
- Examples: Gemmule formation and Budding.
Gemmule Formation in Sponges:
- Definition: Internal bud exclusive to sponges for asexual reproduction during unfavorable conditions.
- Characteristics:
- Gemmule: Mass of dormant archaeocytes.
- Archaeocytes develop into new organism.
- Amoebocytes secrete thick membrane around archaeocytes.
- Process: Gemmules remain dormant until favorable conditions return. Hatch and develop into new individuals.
- Example: Spongilla.
Budding in
Coelenterates and Colonial Ascidians:
- Definition: Simple asexual reproduction method observed in coelenterates (Hydra and corals) and some colonial ascidians.
- Formation: Small outgrowth (bud) develops towards basal end of body.
- Development: Bud grows, forms tentacles, and transforms into new individual. Young Hydra detaches from parent to become separate organism.
Sexual Reproduction in Animals:
- Definition: Offspring produced by fusion of gametes (amphimixes).
- Gamete Formation: Both male and female parents undergo meiosis in gonads.
Phases in Life:
- a) Juvenile Phase/Pro-reproductive Phase: Growth.
- b) Reproductive/Maturity Phase: Sex organ maturation.
Breeding Patterns:
- Seasonal Breeders: Breed only in particular season (e.g., goat, sheep, donkey).
- Continuous Breeders: Breed throughout the year (e.g., human, apes).
Human Reproduction:
- Steps: Gametogenesis - Insemination - Internal Fertilization - Zygote Formation and Embryogenesis - Gestation and Parturition- Lactation
Primary Sex Organs:
- Male: Testes (singular: testis)
- Female: Ovaries (singular: ovary)
Secondary or Accessory Sex Organs:
- Male: Organs other than testis.
- Female: Organs other than ovaries.
Secondary Sexual Characteristics:
- Male: Beard, mustache, chest hair, muscular body, enlarged larynx, etc.
- Females: Developed breasts, broader pelvis, high-pitched voice, etc.
- Sexual Dimorphism:Phenomena identifying sexes externally.
Male Reproductive System:
Parts: Testes - Accessory Ducts – Glands - External Genitalia
1. Testes:
- Position: Located in scrotum.
- Structure: Dimensions: Approximately 4.5 cm length, 2.5 cm width, 3 cm thickness, Contains 200 to 300 lobules with seminiferous tubules.
- Functions: Produce sperm, Secrete male sex hormone, androgen or testosterone.
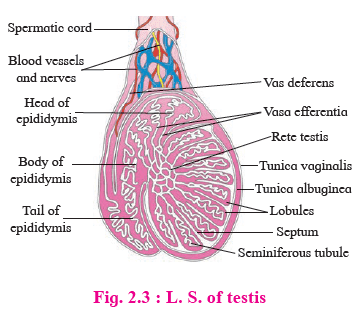
2. Accessory Ducts: Rete Testis - Vasa Efferentia – Epididymis - Vas Deferentia - Ejaculatory Duct - Urethra
a) Rete Testis:
- Position: Posterior side of testis.
- Structure: Formed by convergence of Seminiferous tubules.
- Functions: Carry sperms to vasa efferentia.
b) Vasa Efferentia:
- Position: Arise from rete testis and end into epididymis.
- Structure: 12-20 fine tubules.
- Functions: Carry sperms to epididymis.
c) Epididymis:
- Position: Located on posterior border of each testis.
- Structure: Long, coiled tubes with caput, corpus, and cauda regions.
- Functions: Sperm maturation occurs.
d) Vas Deferentia:
- Position: Enter abdominal cavity through inguinal canal, ascend as spermatic cord.
- Structure: Pair of 40 cm long tubular structures.
- Function: Carry sperm from epididymis to ejaculatory ducts.
e) Ejaculatory Duct:
- Position: About 2 cm long, formed by joining vas deferens and ducts of seminal vesicles.
- Structure: Tube-like structure passing through prostate gland, opening into urethra.
- Functions: Carry seminal fluid containing spermatozoa to urethra.
f) Urethra:
- Position: Extends through penis.
- Structure: About 18-20 cm long tube with urethral orifice.
- Functions: Provides passage for urine and semen.
3. Accessory Glands:
- Components: Seminal Vesicles, Prostate Gland, Cowper’s or Bulbourethral Glands.
- Functions: Secrete fluids aiding reproductive functions.
4. External Genitalia:
- Components: Penis, Scrotum.
- Functions: Copulatory organ (penis), thermoregulator (scrotum).
Terms Associated with External Genitalia of Male:
- Inguinal Canal: Passage for testes descent into scrotum.
- Gubernaculum: Fibro-muscular band in scrotum.
- Cryptorchidism: Failure of testis descent into scrotum causing sterility.
- Erectile Tissues in Penis: Paired Corpora Cavernosa, Median Corpus Spongiosum.
Semen:
- Composition: Viscous, alkaline, milky fluid containing sperm and secretions from epididymis, prostate gland, and Cowper’s glands.
- Rich in: Fructose, Ca++, bicarbonates, prostaglandins.
Histology of Testis:
- External Coverings (L.S.): Outer to inner: Tunica Vaginalis, Tunica Albuginea, Tunica Vasculosa.
- Testicular Structure: Divided into 200-300 testicular lobules by Tunica Albuginea, Each lobule contains 1-4 seminiferous tubules.
- Interstitial Cells of Leydig (Leydig's Cells): Found between seminiferous tubule, Secrete male hormone androgen or testosterone.
- Germinal Epithelial Cells: Cuboidal cells lining seminiferous tubules,
- Sertoli Cells (Sub-tentacular Cells or Nurse Cells): Large pyramidal cells, Provide nutrition to developing sperm.
- Parts: Ovaries - Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts) - Uterus (Womb) - Vagina - External Genitalia (Vulva) - Vestibular Glands - Mammary Glands
1. Ovaries:
- Situated in upper lateral part of pelvis near kidneys.
- Dimensions: About 3 cm length, 1.5 cm breadth, 1.0 cm thickness.
- Solid, oval or almond-shaped.
- Produce ova and hormones (estrogen, progesterone, relaxin, activin, inhibin).
- Control secondary sexual characteristics, menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and parturition.
2. Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts):
- Horizontal over peritoneal cavity.
- Length: 10 to 12 cm.
- Lined by ciliated epithelium.
- Transport ovum from ovary to uterus.
- Subdivisions: a) Infundibulum: With finger-like processes (fimbria), b) Ampulla: Site of fertilization. c) Cornua or Isthmus: Opens into uterus.
Uterus (Womb):
- Pear-shaped, highly muscular, thick-walled, hollow organ.
- Dimensions: About 8 cm length, 5 cm width, 2 cm thickness.
- Three Parts: Fundus, Body (Corpus), Cervix.
- Layers: a) Perimetrium: Outer serous layer. b) Myometrium: Middle thick muscular layer. c) Endometrium: Inner highly vascular mucosa with uterine glands.
- Functions: Receive ovum, develop placenta during pregnancy, expel young at birth.
Vagina:
- Highly distensible fibro-muscular tube between cervix and vestibule.
- Length: 7 to 9 cm.
- Internally lined by stratified, non-keratinized epithelium.
- Functions: Birth canal, copulatory passage, passage of menstrual flow.
- Opens into vestibule with vaginal orifice, may be covered with hymen.
Vestibular Glands (Bartholin’s Glands): Release lubricating fluid into vestibule.
Mammary Glands (Breasts): Accessory organs for production and release of milk after parturition.
Puberty / Sexual Maturity in Females:
Initiation of Puberty:
- Gonadotropins (FSH and LH) secreted by anterior pituitary stimulate ovaries.
- Ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone.
- Hormonal changes bring about secondary sexual characters.
Reproductive Age of Female:
- Period from menarche to menopause.
- Menarche: Beginning of menstrual cycle at 10 to 14 years.
- Menopause: Cessation of reproductive cycles around 45 to 50 years due to hormonal imbalance.
- Histological Structure: Central part: Medulla. Outer part: Cortex.
- Cortex covered by germinal epithelium, medulla contains stroma with blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerve fibers.
- Ovarian Follicle Development:
- Primordial follicles mature into multilayered primary, secondary, and Graafian follicles during menstrual cycle.
- Graafian follicle: Outer layers - theca externa, theca interna, membrane granulosa, filled with antrum containing liquor folliculi.
- Cumulus oophorus or discus proligerus: Small hillock of cells over which ovum is lodged.
- Layers covering ovum: Vitelline membrane, zona pellucida, corona radiata.
- Corpus Luteum:
- Formed from empty Graafian follicle after ovulation.
- Converts into corpus albicans (white body) in absence of conception.
Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
Overview:
- Series of cyclic changes in ovary and uterus.
- Regulated by gonadotropins from pituitary and hormones from ovary.
- Cycles repeated approximately every 28 days.
Phases of Menstrual Cycle and Their Hormonal Control:
1. Menstrual Phase (Day 1-5):
- Occurs in absence of fertilization.
- Uterine endometrium sloughed off.
- Decrease in progesterone and estrogen levels.
- Release of prostaglandins causing endometrial rupture.
- Discharge of blood, tissue fluid, mucus, cellular debris through vagina.
- FSH secretion from pituitary stimulates follicle development.
2. Follicular Phase (Day 5-14):
- Follicles develop in ovary, endometrium proliferates.
- 6 to 12 secondary follicles develop, one becomes Graafian follicle.
- Developing follicles secrete estrogen.
- Estrogen stimulates endometrial regeneration, proliferation.
- Endometrial thickness: 3-5 mm.
3. Ovulatory Phase (Day 14-15):
- Ovulation occurs.
- Mature Graafian follicle ruptures, secondary oocyte released.
- Surge of LH from pituitary triggers ovulation.
4. Luteal Phase (Day 16 to 28):
- Empty Graafian follicle becomes corpus luteum under LH influence.
- Uterine endometrium thickens, becomes more secretory (secretory phase).
- Corpus luteum secretes progesterone, estrogen, inhibin.
- Stimulates growth of endometrial glands, uterine secretions.
- Endometrium becomes more vascularized, 8-10 mm thick.
- Corpus luteum survives for two weeks, then degenerates into corpus albicans if no fertilization.
- If fertilization occurs, hCG secreted by embryo maintains corpus luteum.
- Presence of hCG in blood and urine indicates pregnancy.
- If no fertilization, corpus luteum regresses, new menstrual cycle begins.
- Definition: Formation of gametes in sexually reproducing animals.
- Types of Gametes: Sperm: Male gamete andOvum (Egg): Female gamete.
- Formation of Gametes: From primordial germ cells of gonads.
Spermatogenesis:
- Process of sperm formation.
- Occurs in testis (male gonads) in seminiferous tubules lined by germinal epithelium.
- Nurse cells (or Sertoli cells) provide nourishment to developing sperms.
Phases of Spermatogenesis:
- Multiplication Phase
- Growth Phase
- Maturation Phase
- Spermiogenesis: Spermatids undergo metamorphosis to form mature, motile sperms.
- Increase in sperm length.
- Distinction of centrioles into proximal and distal.
- Formation of axial filament, spirally coiled mitochondria, and acrosome from Golgi complex.
Structure of Sperm (Spermatozoa):
- Microscopic, elongated haploid motile male gamete.
- Measures about 0.055 mm in length.
- Produced by spermatogenesis.
- Viability: 72 hours, fertilization potential: 12 to 14 hours.
- Parts of Sperm: Head, Neck, Middle Piece, Tail.
1. Head:
- Main part, flat and oval.
- Contains large nucleus and acrosome.
- Acrosome: Derived from Golgi complex, secretes hyaluronidase for egg penetration.
- Covered by a fibrillar sheath.
2. Neck:
- Short region with two centrioles.
- Proximal centriole aids in first cleavage of zygote.
- Axial filament formed by distal centriole.
3. Middle Piece:
- Functions as powerhouse for sperm.
- Contains many spirally coiled mitochondria.
- Mitochondria supply energy for sperm's movement (1.5 to 3 mm per minute).
- Covered by a sheath along with posterior half of nucleus and neck.
4. Tail:
- Long, slender, tapering structure.
- Formed of cytoplasm.
- Contains axial filament and nine accessory fibers surrounding two central longitudinal axial filaments.
- Tail lashes, aiding spermatozoa's swimming.
Oogenesis: Process in the ovary leading to the formation of the secondary oocyte.
Phases of Oogenesis:
- Phase of Multiplication: Oogonia formation in large numbers.
- Phase of Growth: One oogonium enlarges, becoming a primary oocyte.
- Phase of Maturation:
- Primary oocyte undergoes meiosis I, forming a large haploid secondary oocyte.
- Unequal cytoplasmic division: secondary oocyte and polar bodies.
- Rounded, haploid, non-motile, largest cell in the body (0.1 mm diameter).
- Microlecithal, almost yolk-free.
- Abundant cytoplasm with a large eccentric nucleus surrounded by a vitelline membrane.
- Centriole absent.
- Exhibits polarity: animal pole (with polar body and nucleus) and vegetal pole.
- Enclosed by zona pellucida (inner, thin, non-cellular) and corona radiata (outer, thick, cellular).
- Perivitelline space between vitelline membrane and zona pellucida.
- Zona pellucida secreted by the ovum, corona radiata formed by follicular cells.
- Fertilization: Fusion of haploid male and female gametes into a diploid zygote.
- Location: Internal, occurs in the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
- Capacitation of Sperms: Sperms move towards the secondary oocyte.
- Release of Acrosomal Enzymes: Sperm head releases enzymes upon contact with the secondary oocyte.
- Separation of Corona Radiata Cells: Acrosomal enzymes like hyaluronidase dissolve cells of the corona radiata.
- Compatibility Reaction: Fertilizin (egg) binds with antifertilizin (sperm). Zona pellucida of the egg has fertilizin receptor proteins (ZP3, ZP2). Acrosome ruptures, releasing acrosin / zona lysin.
- Acrosome Reaction: Acrosin dissolves zona pellucida and vitelline membrane at the contact point of the sperm head.
- Entry of Sperm Nucleus into Ovum: Sperm nucleus and centriole enter the ovum.
- Formation of Fertilization Membrane / Cortical Reaction: Vitelline membrane of the ovum converts into a fertilization membrane, preventing polyspermy.
- Activation of Ovum: Completion of meiosis-II of the secondary oocyte occurs. Ovum receives the centriole from the sperm, completing meiosis-II and releasing the second polar body.
- Syngamy / Karyogamy: Fusion of male pronucleus and female pronucleus. Synkaryon formed after fusion of male and female nuclei.
- Formation of Diploid Zygote:Concludes the process of fertilization.
Significance of Fertilization:
- Forms Zygote: Fertilization creates the zygote, which develops into new offspring.
- Restores Diploid Chromosomes: Two haploid gametes merge during fertilization, restoring the diploid number of chromosomes in the zygote.
- Completion of Oogenesis: Fertilization passes on centrioles to the ovum, allowing the secondary Oocyte to complete meiosis-II, concluding the process of oogenesis.
- Genetic Variation: Fertilization mixes the genetic characters of two parents, leading to variation and playing a role in evolution.
- Determines Sex: Fertilization determines the sex of the offspring.
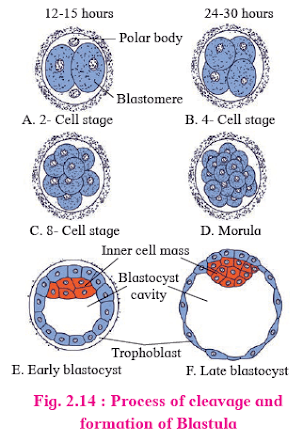
- Rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote to form a hollow spherical multicellular blastula.
- Begins as the zygote passes through the fallopian tube.
- Holoblastic, equal, and indeterminate in humans.
- Daughter cells are called blastomeres.
- Formation of a hollow, multicellular blastocyst from the 16-32 celled morula stage.
- Blastocyst reaches the uterus and absorbs glycogen-rich uterine milk.
- Outer layer forms trophoblast, inner cells form inner cell mass or embryoblast.
- Blastocyst size doubles from 0.15 mm to 0.30 mm.
- Trophoblast cells flatten, forming a blastocyst cavity.
- Rauber's cells are trophoblast cells in contact with the embryonal knob.
- Embedding of the blastocyst in the uterine endometrium for further gestation.
- Occurs on the 7th to 10th day after fertilization.
- Trophoblast divides into cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast, aiding in burying the blastocyst in the endometrium.
5. Gastrulation:
- Definition: Formation of gastrula from the blastocyst, starting around 8 days after fertilization.
- Events during Gastrulation:
- Differentiation of blastomeres: Rearrangement of blastomeres forms three germinal layers.
- Morphogenetic movements: Cells move to their destined areas of differentiation.
Sequential Changes in Gastrulation:
- Formation of endoderm
- Formation of embryonic disc
- Formation of amniotic cavity
- Formation of ectoderm
- Formation of mesoderm
- Formation of extra-embryonic coelom
- Formation of chorion and amnion
Organogenesis: Process of forming organs after gastrulation.
Fate of Germinal Layers (Histogenesis):- Ectoderm: Epidermis, sweat glands, lens, nervous system, etc.
- Mesoderm: Muscles, connective tissue, circulatory system, kidney, etc.
- Endoderm: Epithelium of gut, glands of stomach, lungs, liver, pancreas, etc.
Pregnancy / Gestation:
- Definition: Condition of developing foetus in the uterus.
- Duration: About 280 days in humans, divided into three trimesters of three months each.
Three Trimesters:
1. First Trimester: (From fertilization to 12th week)
- Radical changes in mother's body and embryo.
- Organogenesis occurs.
- Embryo becomes a rudimentary foetus (~3 cm long) by eight weeks.
- Major organs, limbs, CNS, and circulatory system develop.
- Maternal progesterone levels rise, suspending menstrual cycle.
- Foetus reaches ~7-10 cm by trimester end.
- Mother may experience morning sickness.
2. Second Trimester: (From 13th to 26th week)
- Foetus grows to ~30 cm.
- Pregnancy becomes visually apparent.
- Hormone levels stabilize, placenta takes over progesterone production.
- Foetus develops hair, eyebrows, eyelashes, pinnae.
- Baby's movements felt by mother.
- Foetus reaches half the size of a newborn.
3. Third Trimester: (From 27th week till parturition)
- Foetus grows to ~50 cm and 3-4 kg.
- Uterus expands, compressing maternal organs.
- Mother experiences frequent urination, digestive issues, back strain.
- Foetus fully developed and ready for parturition.
Placenta:
- Definition: Flattened, discoidal organ attached to uterine wall and baby's umbilical cord.
- Functions: Facilitates nutrient and oxygen exchange, removes waste.
- Formation: Combination of foetal chorionic villi and maternal uterine wall.
- Type: Human placenta is haemochorial (foetal villi and maternal tissue).
- Endocrine Function: Produces hormones like hCG, progesterone, estrogen, and relaxin.
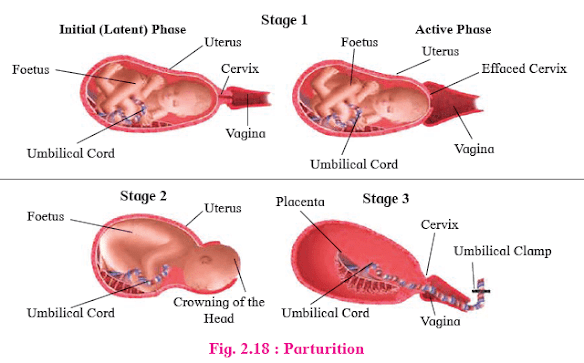
- Definition: Birth process accompanied by labour pains.
- Neuro-endocrine Mechanism: Rise in estrogen:progesterone ratio, Increase in oxytocin receptors in uterine wall.Stages:
- Uterine contractions start, moving baby toward cervix.
- Oxytocin secretion causes severe uterine contractions.
- Cervix and vagina dilate, amniotic sac
ruptures.
- Stronger uterine and abdominal contractions.
- Foetus moves head down through cervix and vagina.
- Umbilical cord tied and cut.
- Placenta separates from uterine wall and expelled.
- Uterine contractions continue.
Lactation: Nourishment of newborn through milk.
- Mammary glands become functional.
- First milk called colostrum, rich in proteins and antibodies.
- Neuroendocrine process involving various maternal glands.
Distinguish between Asexual and Sexual Reproduction:
- Definition: Total wellbeing of emotional, behavioural, physical, and social aspects related to reproduction.
- Initiatives in India: Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) programmes, National-level action plans for improving reproductive health.
- Objectives: Control population growth, Improve awareness and facilities for reproductive health, Reduce infertility, infant mortality, and maternal mortality rates.
Goals of RCH Programmes:
- Create awareness about reproduction.
- Provide reproductive health facilities.
- Support for a reproductively healthy society.
- Reduce infertility, infant, and maternal mortality rates.
Achieving RCH Goals:
- Sex Education: Introduce in schools covering safe practices, STDs, adolescent issues.
- Media Awareness: Use audio-visual and print media for dissemination.
- Birth Control Education: Educate youth about contraception, prenatal, and postnatal care.
- Population Control Awareness: Highlight problems of uncontrolled growth, sex crimes prevention.
- Ban Awareness: Educate on statutory bans like amniocentesis for sex determination.
- Immunization Awareness: Promote child immunization programmes.
Types of Contraceptive Methods:
- Natural Method/Safe Period/Rhythm Method: Avoiding intercourse around ovulation (14th day of menstrual cycle).
- Coitus Interruptus or Withdrawal: Withdrawal of penis before ejaculation.
- Lactational Amenorrhoea: Intense lactation post-parturition inhibits ovulation.
- Chemical Means (Spermicides): Foam, tablets, jellies, or creams immobilize and kill sperm.
- Condom: Thin rubber sheath covering the penis; prevents STDs and AIDS.
- Diaphragm, Cervical Caps, and Vaults: Rubber devices inserted into the vagina to cover the cervix.
- Intra-uterine Devices (IUDs): Plastic or metal objects placed in the uterus; prevent fertilization or embryo implantation.
- Oral Contraceptive Pills: Inhibit ovulation by suppressing FSH and LH secretion.
- Birth Control Implant: Implanted under the skin of the upper arm; similar to oral contraceptives.
3. Permanent Methods:
- Sterilization: Surgical procedures for permanent contraception.
- Male Sterilization (Vasectomy): Cutting and sealing the vas deferens.
- Female Sterilization (Tubectomy): Blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes.
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP):
- Definition: Intentional termination of pregnancy before full term.
- MTP is induced abortion.
- Indirectly controls population.
- Legalized in India since 1971.
- Performed for discontinuing unwanted pregnancies or due to foetal defects.
- Aborting healthy female embryos is illegal.
- Safely done only during the first trimester.
Amniocentesis:
- Process of collecting amniotic fluid containing foetal cells for chromosome analysis.
- Done to check for foetal abnormalities.
- Sex determination by amniocentesis is legally banned in India.
PC-PNDT Act (2003):
- Mandates:
- Prohibition of sex selection before or after conception.
- Regulation of pre-natal diagnostic techniques.
- Prevention of misuse for sex determination leading to female foeticide.
- Aimed at banning sex selection techniques and preventing misuse of pre-natal techniques for sex-selective abortions.
- Essential for preventing female foeticides and improving the sex ratio in India.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs):
- Definition: Infections transmitted through sexual intercourse.
- Also known as Venereal Diseases (VDs) or Reproductive Tract Infections (RTIs).
- Major diseases include syphilis and gonorrhoea.
- Caused by: Spirochaete bacterium Treponema pallidum.
- Transmission Modes: Sexual intercourse, kissing, close body contact. Mothers can transmit to newborns (Congenital syphilis).
- Symptoms: Primary lesion called chancre at infection site. Skin rashes, fever, inflamed joints, hair loss. Paralysis, degenerative changes in heart and brain.
- Preventive Measures: Sex education, hygiene, avoiding sex with unknown partners. Condom use during intercourse.
- Treatment: Prompt treatment with Penicillin.
Gonorrhoea:
- Caused by: Diplococcus bacterium, Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- Transmission Modes: Sexual contacts, infested clothes. Incubation period: 2-14 days in males, 7-21 days in females.
- Symptoms (Males): Partial urethral blockage, pus from penis, pain during urination, arthritis.
- Symptoms (Females): Pelvic inflammation, urinary tract issues, sterility, arthritis.
- Preventive Measures: Sexual hygiene, condom use. Avoiding sex with unknown or multiple partners.
- Treatment: Cefixime antibiotic.
Infertility:
- Definition: Inability to conceive naturally after one year of regular unprotected intercourse.
- Options for infertile couples:
- Fertility drugs
- Test tube babies
- Artificial insemination
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
- Surrogate motherhood
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Fertilization outside the body, with the embryo later transferred to the mother's body (test-tube baby).
- Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT): Transfer of the embryo into the fallopian tubes.
- Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT): Transferring donor ovum to another female's fallopian tube acting as a surrogate mother.
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): Injection of single sperm directly into an ovum's cytoplasm in the laboratory.
- Artificial Insemination (AI): Introduction of collected sperms into the female cervix for in vivo fertilization.
- Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI): Similar to AI, but sperms are introduced into the uterine cavity.
- Sperm/Semen Bank: Collection and storage of sperms for needy couples via cryopreservation.
- Adoption: Legal adoption of a child by a couple or single parent.
- Surrogate Mother: Implantation of embryo in a woman who acts as a surrogate, not the biological mother.
Impact of Substance Use on Infertility:
- Tobacco/Nicotine: Blocks sperm production, reduces testicle size.
- Alcoholism: Interferes with testosterone synthesis, impacts sperm count.
- Cocaine/Marijuana: Reduces sperm count and quality temporarily.






















0 Comments